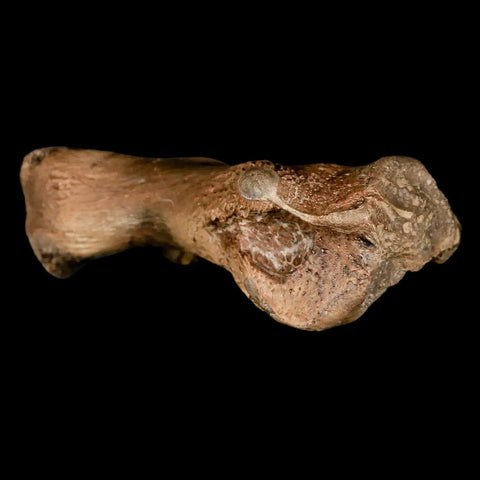
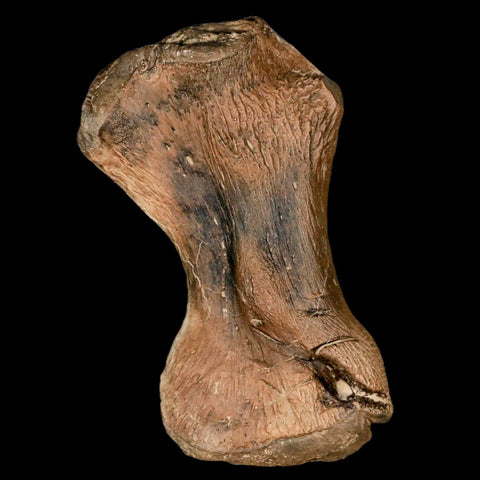
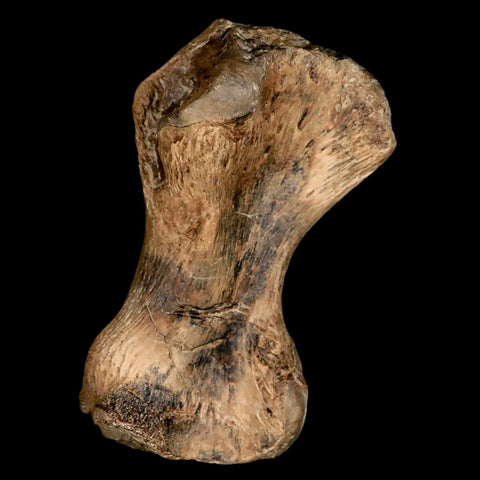
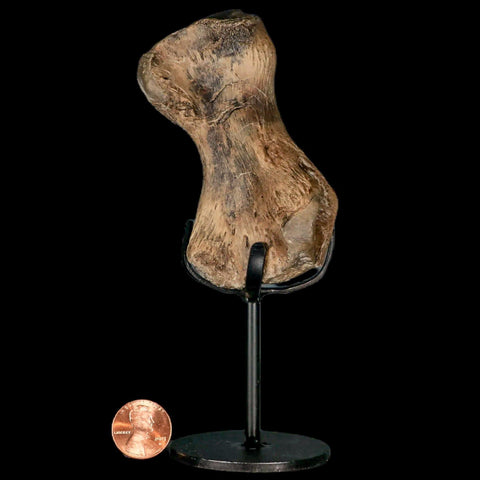
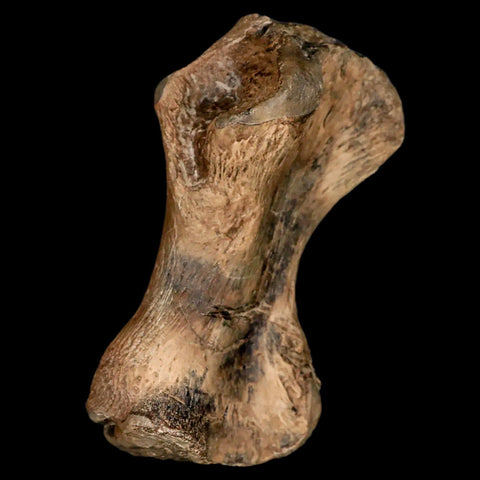
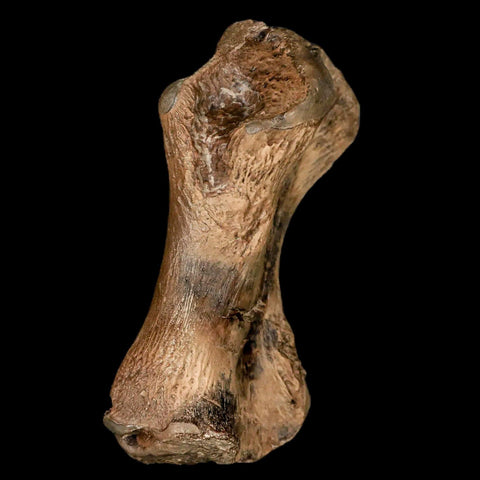
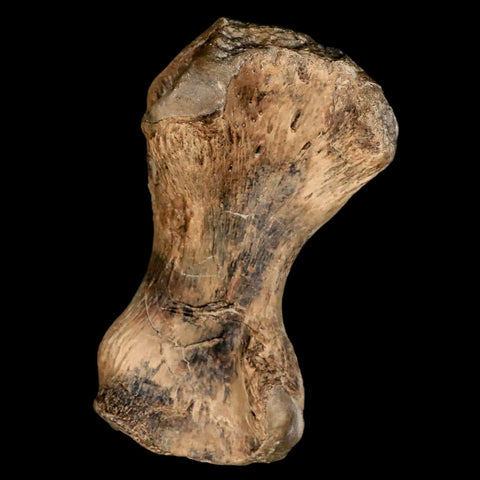
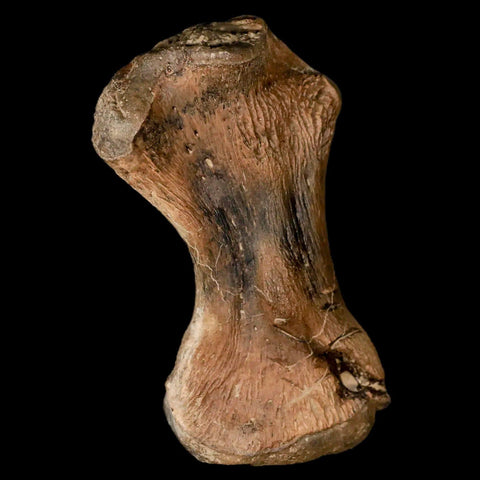
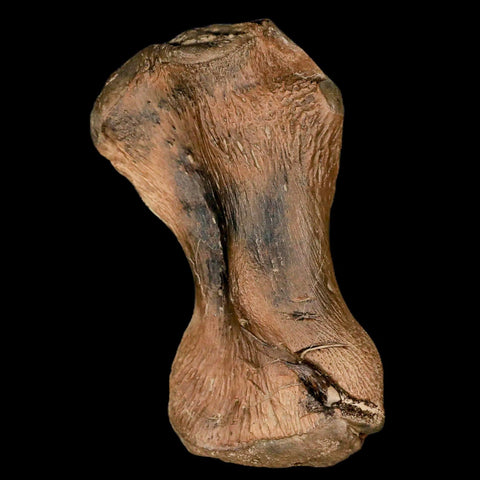
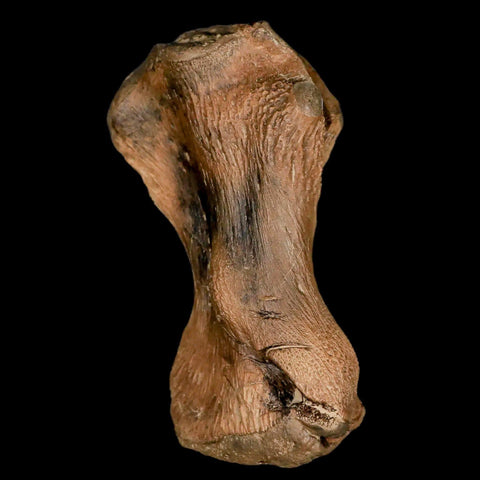
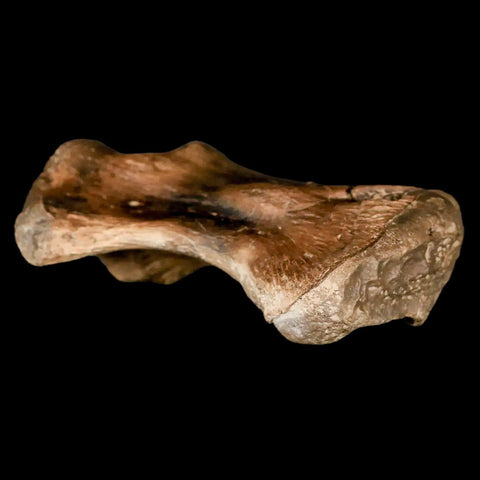
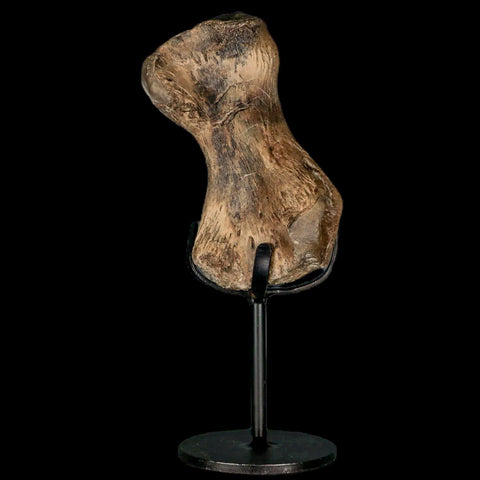
3.4" Toxochelys Sp Humerus Fossil Turtle Limb Bone Bite Marks Cretaceous Age Texas
Location: Ozan Formation. Fannin County, Texas
Weight: 6.8 Ounces (With Metal Stand)
Dimensions: 5.4 Inches Long, 2.5 Inches Wide, 2 Inches Thick (With Metal Stand)
Dimensions: 3.4 Inches Long, 2 Inches Wide, 1.3 Inches Thick
Comes with a Free Custom Metal Stand.
The item pictured is the one you will receive.
This is a genuine fossil.
Toxochelys Sp is an extinct genus of sea turtles that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 75-70 million years ago. Toxochelys species were relatively small compared to modern sea turtles, with a shell length ranging from about one to two meters. These turtles had a streamlined body shape adapted for swimming in the ancient oceans they inhabited. Toxochelys is known from fossil remains found in North America, particularly in regions such as Texas and Kansas.
Toxochelys is classified within the family Cheloniidae, which includes modern sea turtles. The genus Toxochelys is characterized by its unique shell morphology, which features a combination of bony plates (osteoderms) and cartilage. This shell structure provided Toxochelys with protection while also allowing for flexibility and agility in the water.
Toxochelys likely fed on a diet consisting mainly of small marine organisms such as mollusks, crustaceans, and fish. Its streamlined body and flipper anatomy suggest that it was an efficient swimmer capable of catching prey in the open ocean.
The extinction of Toxochelys, along with many other marine reptiles, occurred at the end of the Cretaceous period around 66 million years ago. The exact cause of their extinction remains uncertain, but factors such as climate change, competition with other marine species, and possibly the impact of a large asteroid or comet are thought to have played a role